(→Basic atomic information) |
Revision as of 21:40, 16 August 2009
Output File Formats in MD++
This tutorial describes the formats of MD++ output files. The most frequently used file in MD++ is the configuration (.cn) file describing atomic positions (and other attributes). Also used a lot is the property (.out) file produced by Molecular Dynamics simulations. MD++ can also read and write VASP (POSCAR) and LAMMPS files.
Contents |
Configuration .cn File
In MD++, we save the current atomic configuration (in memory) to a file using the following command.
finalcnfile = myfile.cn writecn
(This is what we write in a .script input file. If we use .tcl input file, we need to put MD++ at the beginning of the line.)
The atomic configuration can be read into MD++ later (either in the same simulation run or in a different run) using the following command.
incnfile = myfile.cn readcn
Different amount of details are saved into the file, depending on two flags: writevelocity and writeall. By default, writevelocity = 0 and writeall = 0.
Overall format
The saved .cn files have the following format.
The first line is the number of atoms NP.
This is followed by NP lines of data, each corresponding to an atom (more explanation below).
After that, there is a 3x3 matrix H whose column vectors are the three repeat vector of the supercell.
The next line contains the number of species and the name of the species. By default, the number of species is 1 and the name of the species is "Mo". The species name can be set in the input file by, e.g. element0 = "Si", element1 = "C". The species names will not be used by the simulation. Even if you forgot to set them, the simulation can still run correctly.
The last line contains two numbers: zeta and zetav. These are variables used in the Nose-Hoover thermostat. We save them to enhance reproducibility of MD simulations from a saved .cn (restart) file. These values are zero if the file is saved after quasi-static simulations.
Basic atomic information
When writeall = 0 and writevelocity = 0 (default), each line in the saved .cn file (from line 2 to line NP + 1) has the following format.
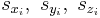
They are the scaled coordinates of atom i.
If we let 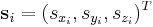 be the scaled coordinate vector of atom i and let
be the scaled coordinate vector of atom i and let 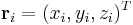 be the real coordinate vector, then they are related to each other by,
be the real coordinate vector, then they are related to each other by,
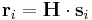
When writeall = 0 and writevelocity = 1, the saved cn files have the following format.